The first thing needed is an assessment of what’s wrong. My advice is to meet with each member of the team individually, make your own assessment of the information you are receiving. A few key dimensions to collect and assess are team structure, individual assignments and roles (whether the team has the right skill sets, are they motivated in their roles and are there any prevalent bad attitudes), and leadership style within the team. Also note the current success and failures of the team.
What has worked well for me in the past is to define a mission statement for the team – what are we trying to do and why? Each member of the team should be able to state and defend the mission and why its critical. A shared understanding and buy in is critical for the team to rally around and cooperate. Remember the Star Trek Enterprise episodes always started with their mission statement – “Space, the final frontier. These are the voyages of the starship Enterprise. Its 5-year mission: to explore strange new worlds, to seek out new life and new civilizations, to boldly go where no man has gone before.”
Define SMART (first defined at GE) and Stretch goals. Smart goals are specific, measurable, achievable, realistic and timeline based. Stretch on the other hand may appear to be more than possible, but are the ones that spark remarkable innovations.
Setup team norms that ensure psychological safety (Charles Duhigg – Smarter, Faster, Better – The Transformative Power of Real Productivity). The following is an excerpt from the book that describes this concept and some of the other critical building blocks for a high performing team: A team climate characterized by interpersonal trust and mutual respect in which people are comfortable being themselves.
1. Teams need to believe that their work is important.
2. Teams need to feel their work is personally meaningful.
3. Teams need clear goals and defined roles.
4. Team members need to know they can depend on one another.
5. But, most important, teams need psychological safety.
Where “Psychological safety” is a shared belief, held by members of a team, that the group is a safe place for taking risks. It is a sense of confidence that the team will not embarrass, reject, or punish someone for speaking up.
Next address the tactical issues of failures and risks. Secure stakeholder agreements to ensure that targets are achievable. Reassign or repurpose team members with bad attitudes.
Some general principles that have helped me throughout my career are as follows –
- Keep criticism private
- Roll up your sleeves and get in the trenches
- Achieve short term wins; Praise achievements and celebrate
- Inspire and motivate – “We can and We will”
Finally measure what you value and put it in a cycle for continuous improvement.
For example, for an IT team, the metrics to measure may be the following:
- Cadence of delivery
- Delivery throughput
- Quality of code delivered
- Stability of the application/platform/system
- Scalability
- Usability measure
- Business continuity
- TCO – total cost of ownership
While for a product team, you may want to measure and improve these:
- Effective product lifecycle management
- Product market position
- Rate of new / modified products being introduced
- Success rate for new / modified products
- Ability to deco/sunset loss making products
Or for an Operations team, the following may be relevant measures:
- Cost per unit work
- Quality per unit work and rework %
- Risk mitigation/avoidance and quality tolerance
- Average turnover in the team and morale
As always, feedback is always welcome…


 tickets early in the morning on Sunday June 17th, and the rest of the day went in team setup, practice runs and calibration & tuning the robotics programs.
tickets early in the morning on Sunday June 17th, and the rest of the day went in team setup, practice runs and calibration & tuning the robotics programs.
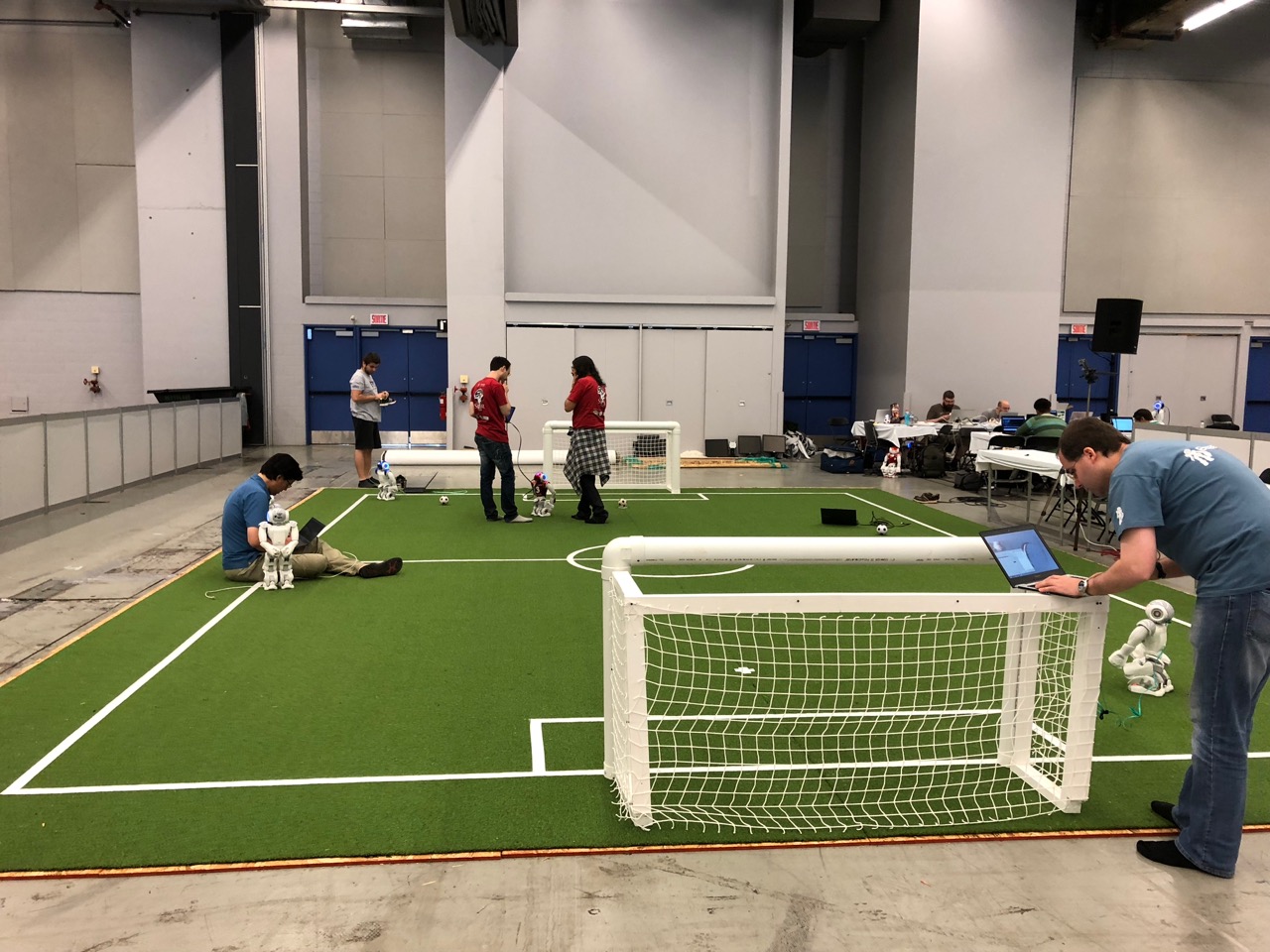
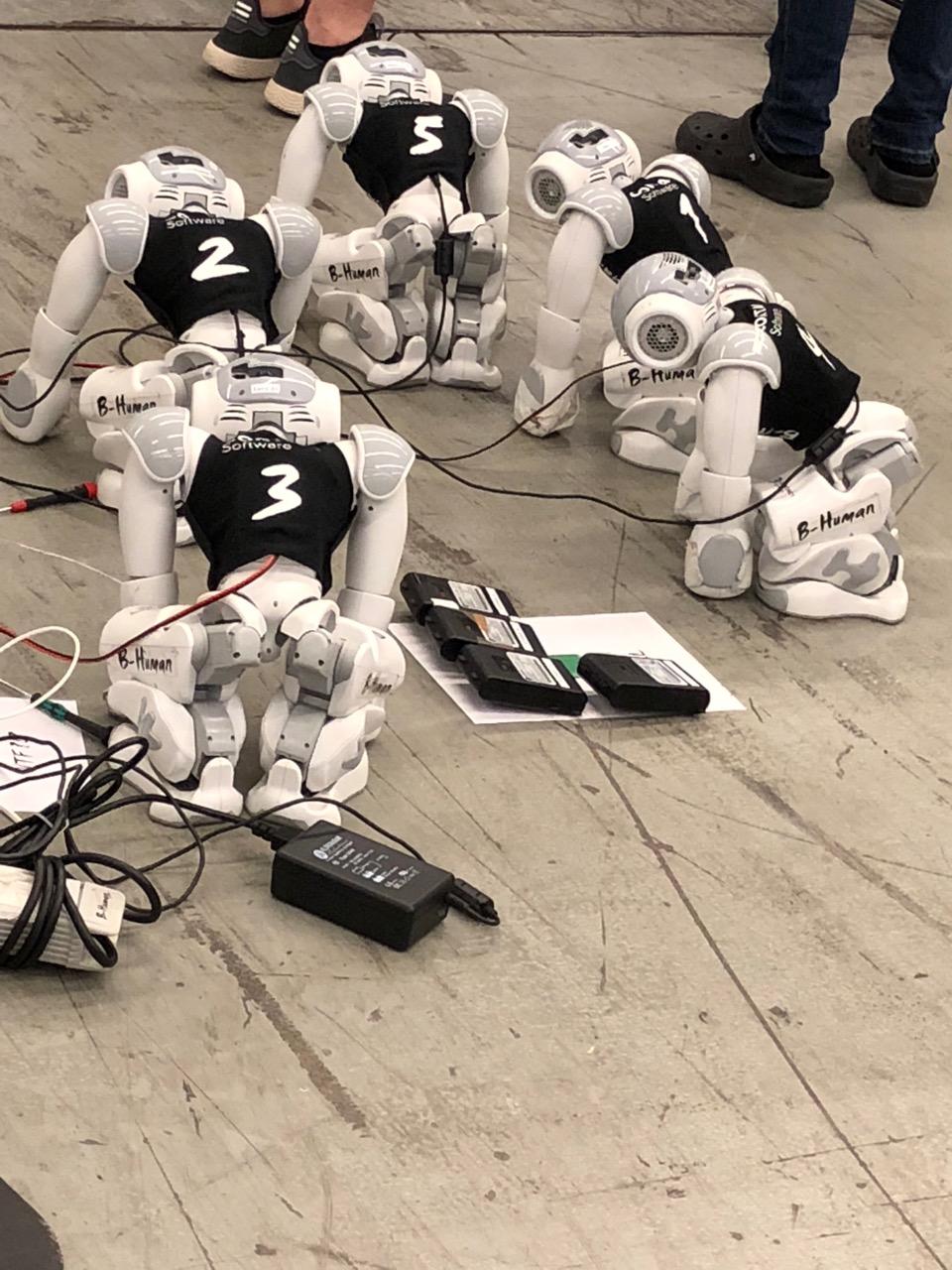
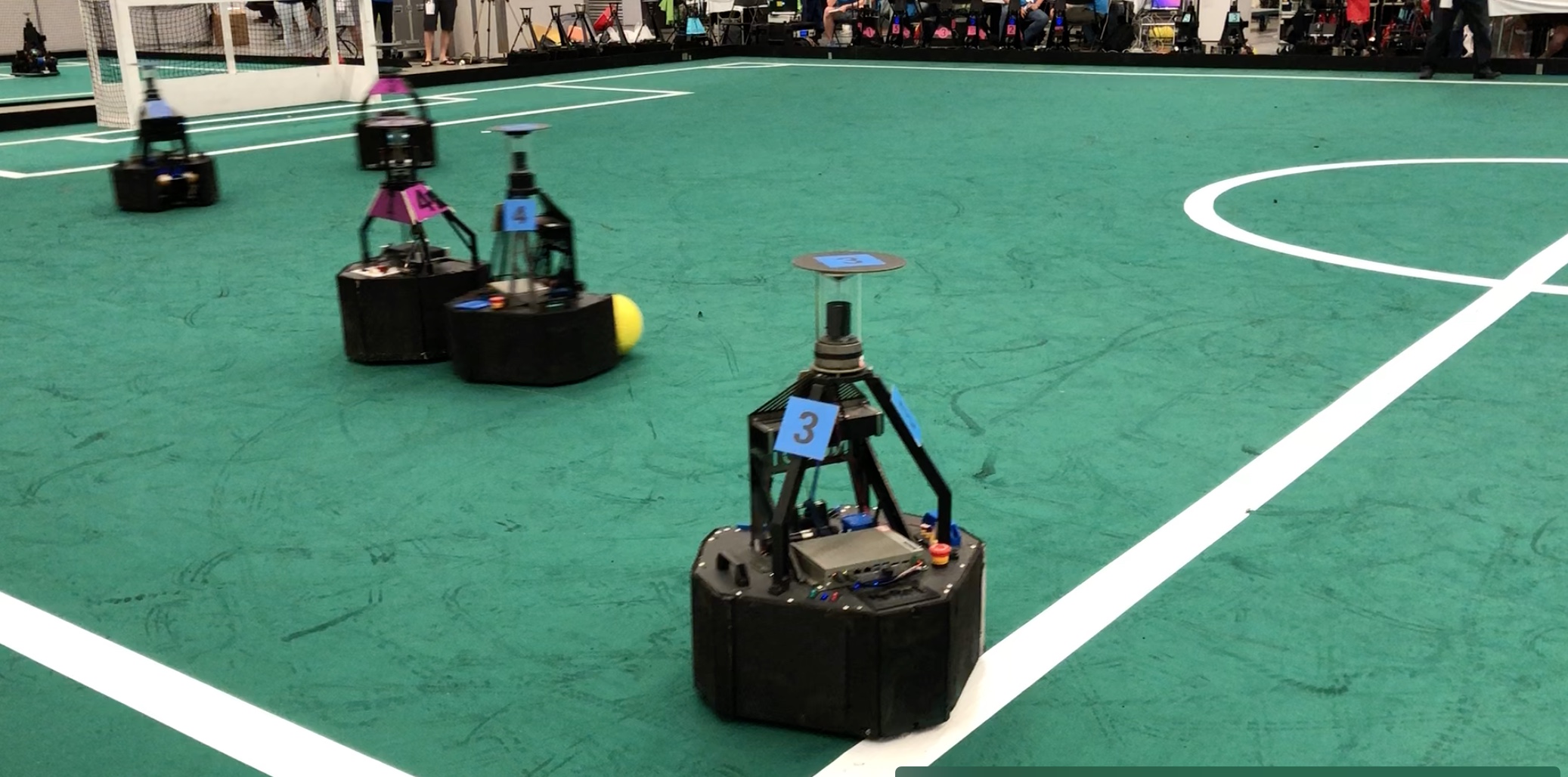










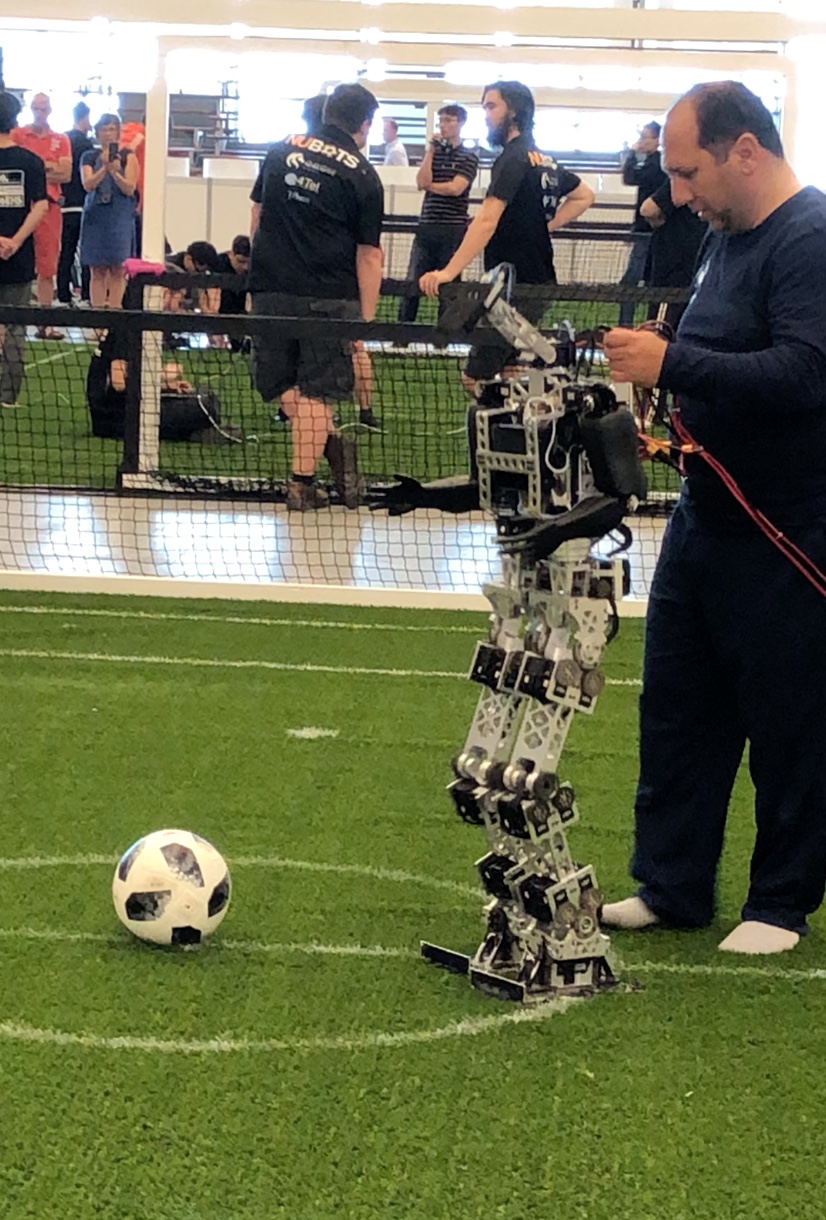
 goal from one of the teams.
goal from one of the teams.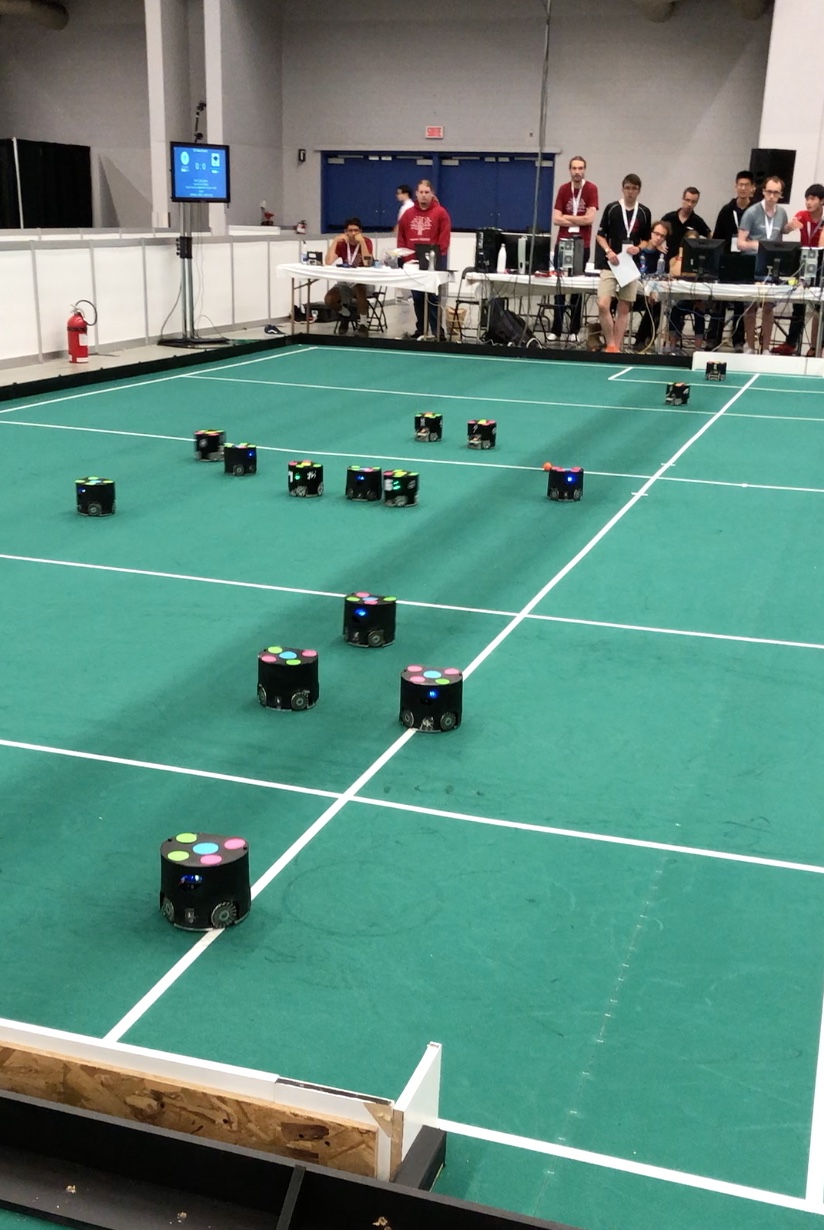 A very fast paced soccer game with bots acting in coordination as one team against an opposing team. Here’s a video that shows how exciting this can be.
A very fast paced soccer game with bots acting in coordination as one team against an opposing team. Here’s a video that shows how exciting this can be.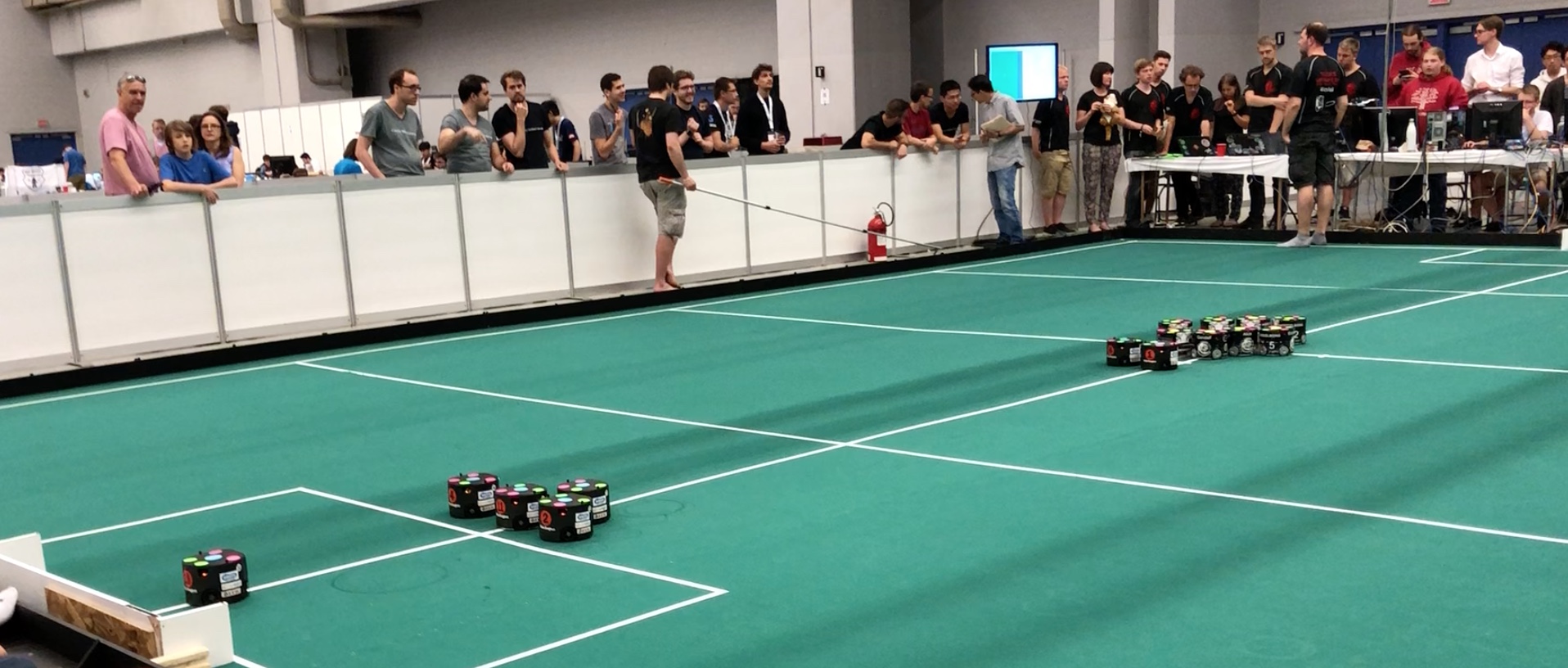
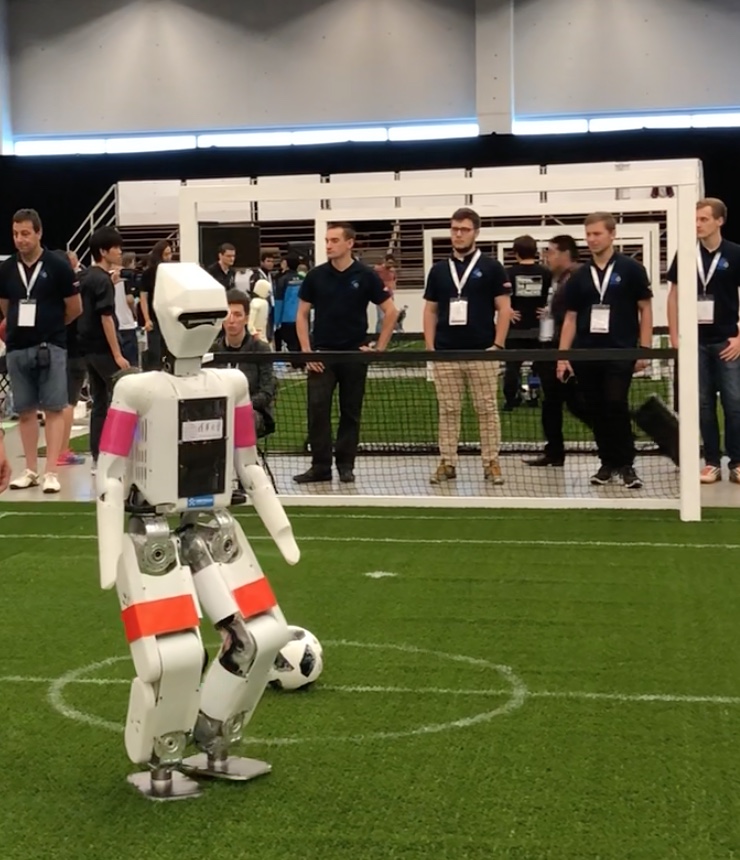
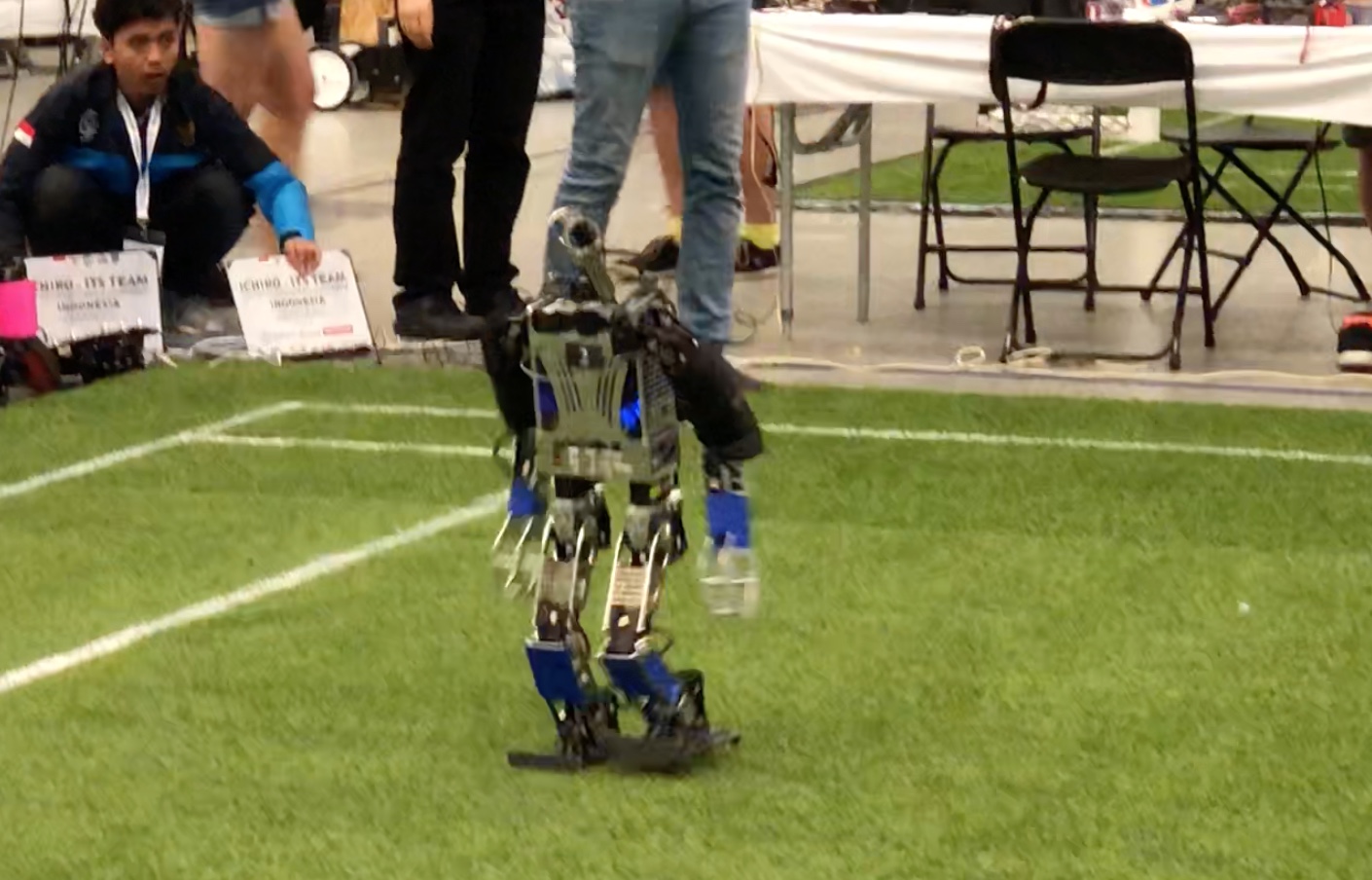
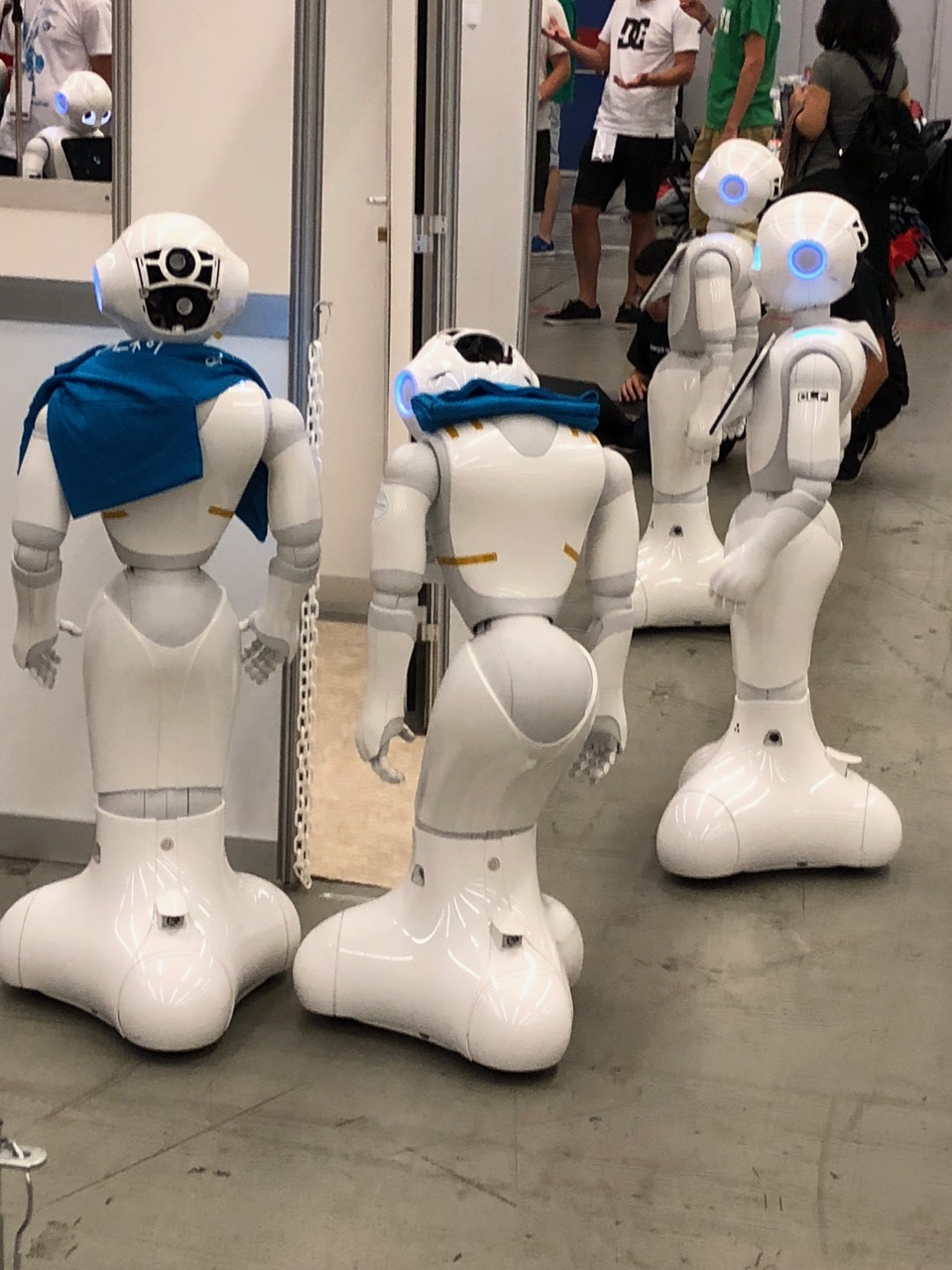


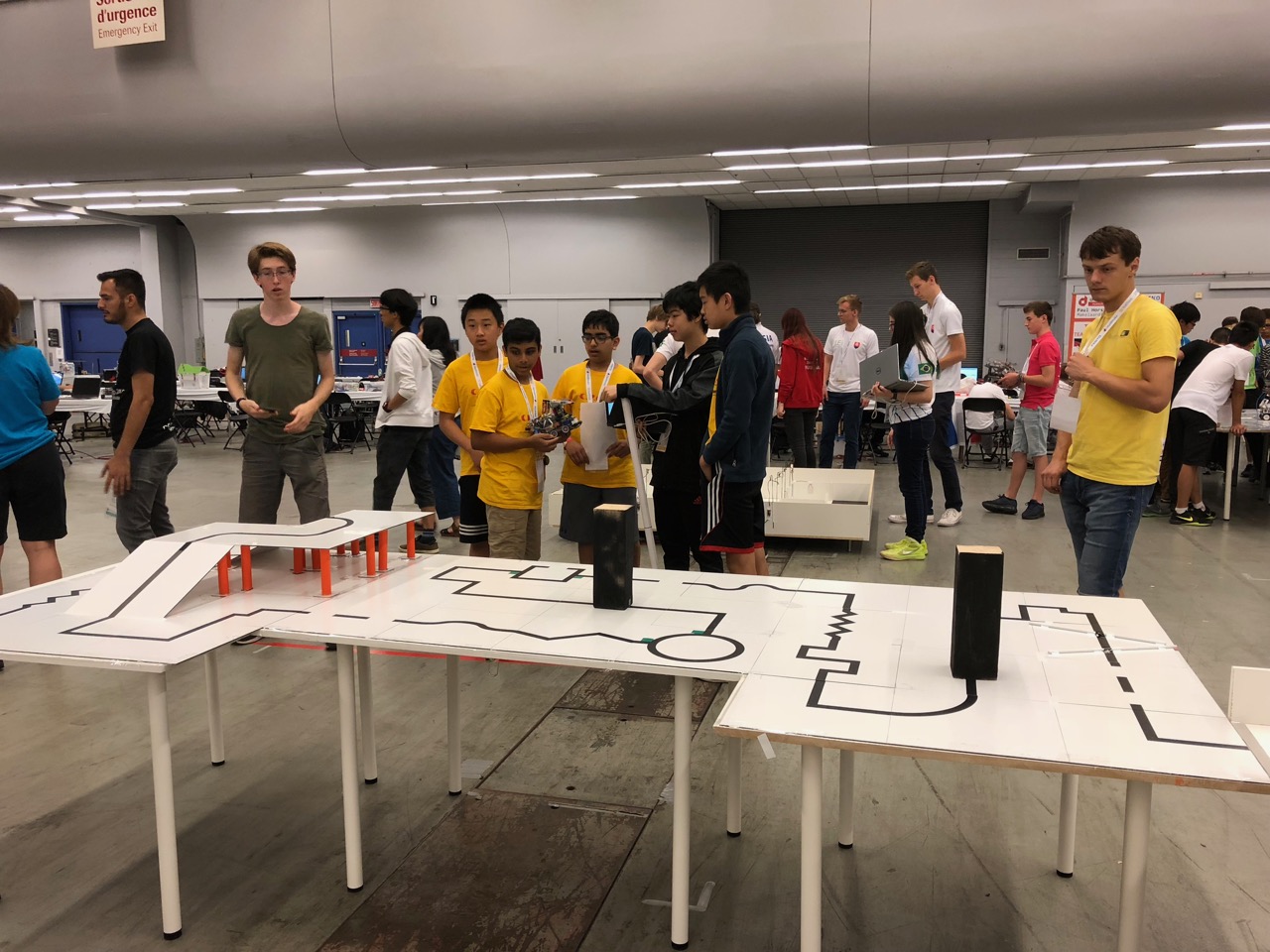
 There were a number of other home setting
There were a number of other home setting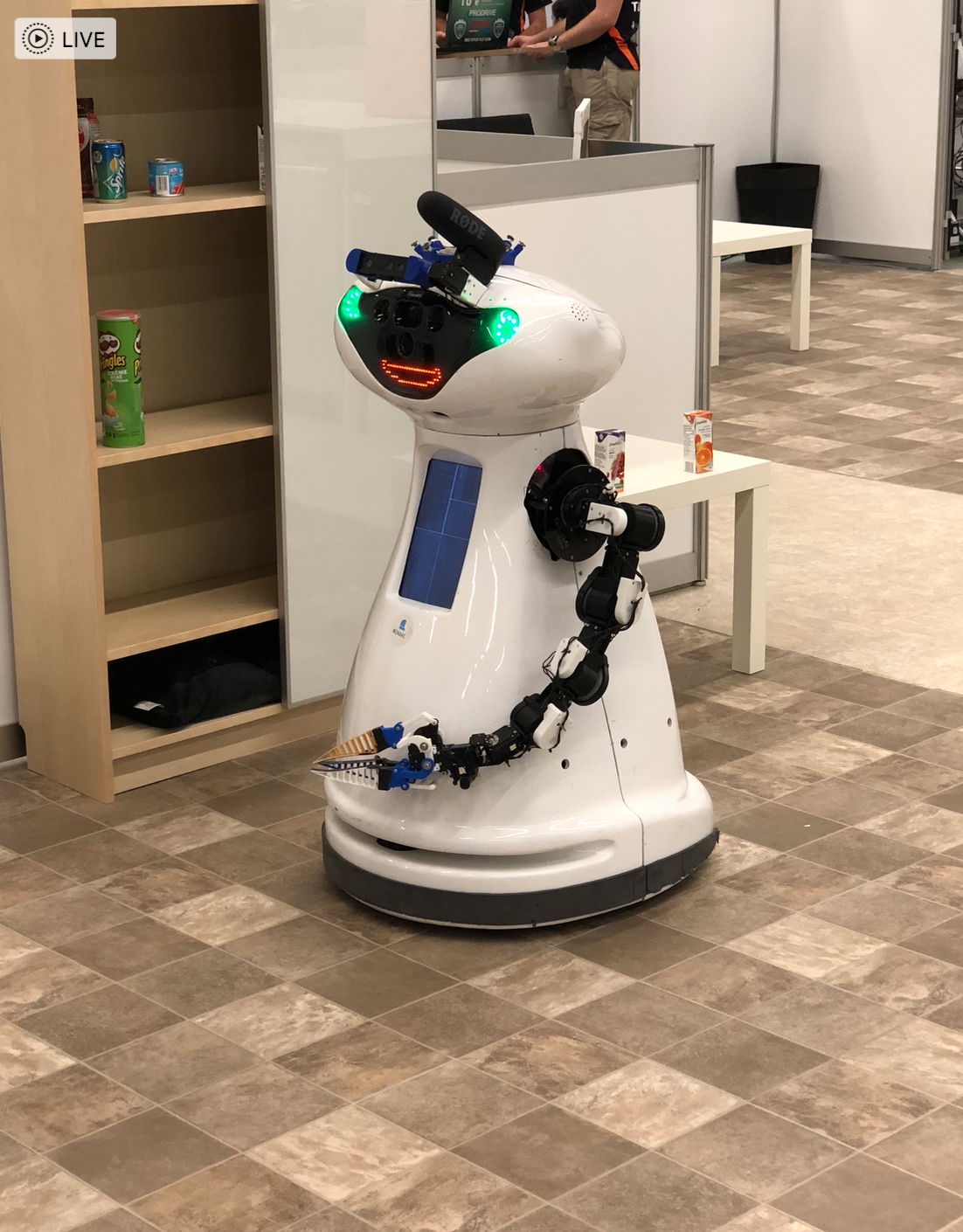  challenges as well – for example unloading grocery bags and storing them in the right location/shelf in a home.
challenges as well – for example unloading grocery bags and storing them in the right location/shelf in a home.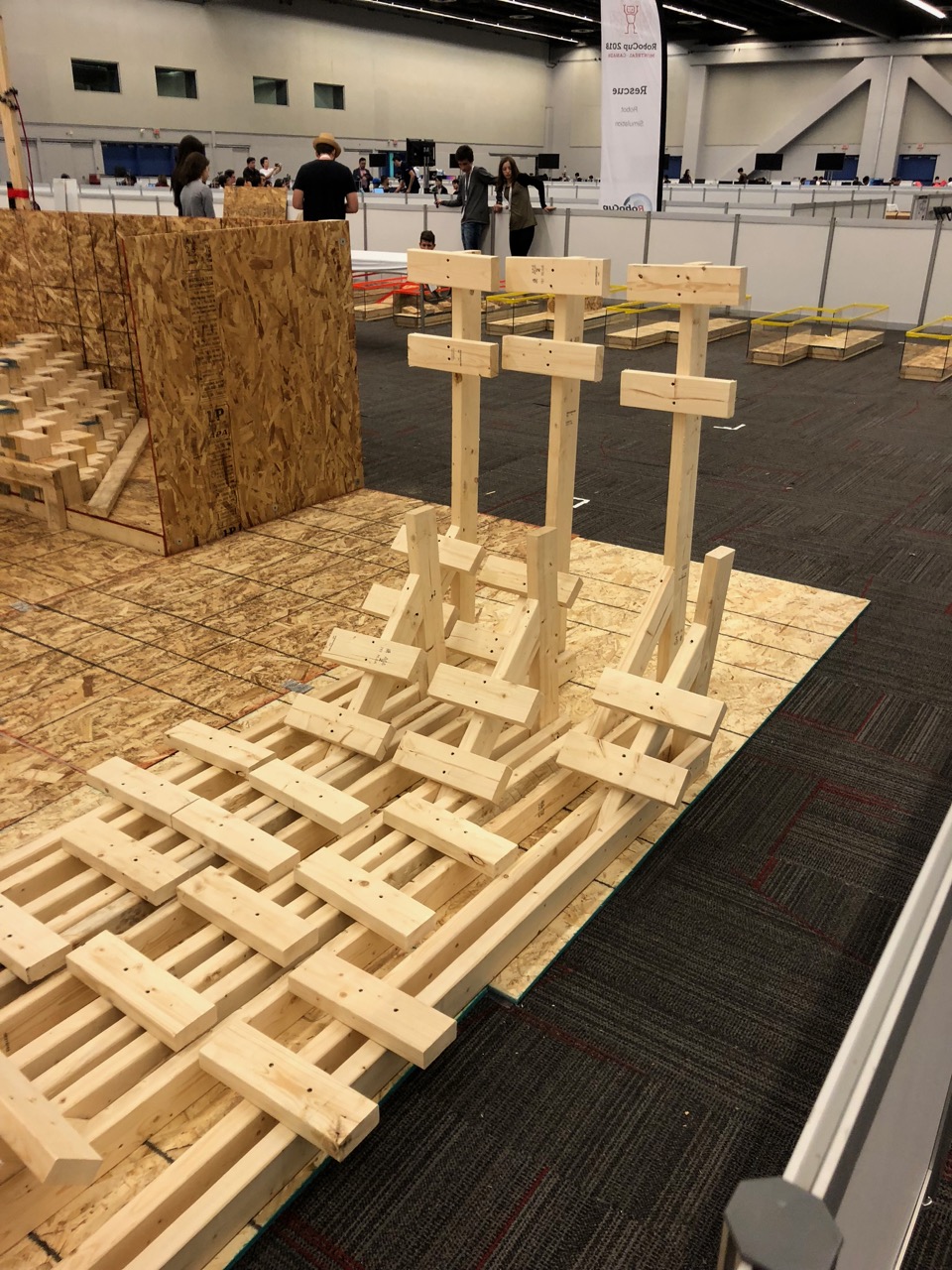 bots can be used in a hazardous situation for rescue. Challenges included navigating difficult terrains, opening doors, accomplishing tasks such as sensor readings, mapping a maze or path through the field etc. Some videos listed here are very impressive. These teams were mainly university and research lab teams. Do check out the following links.
bots can be used in a hazardous situation for rescue. Challenges included navigating difficult terrains, opening doors, accomplishing tasks such as sensor readings, mapping a maze or path through the field etc. Some videos listed here are very impressive. These teams were mainly university and research lab teams. Do check out the following links.
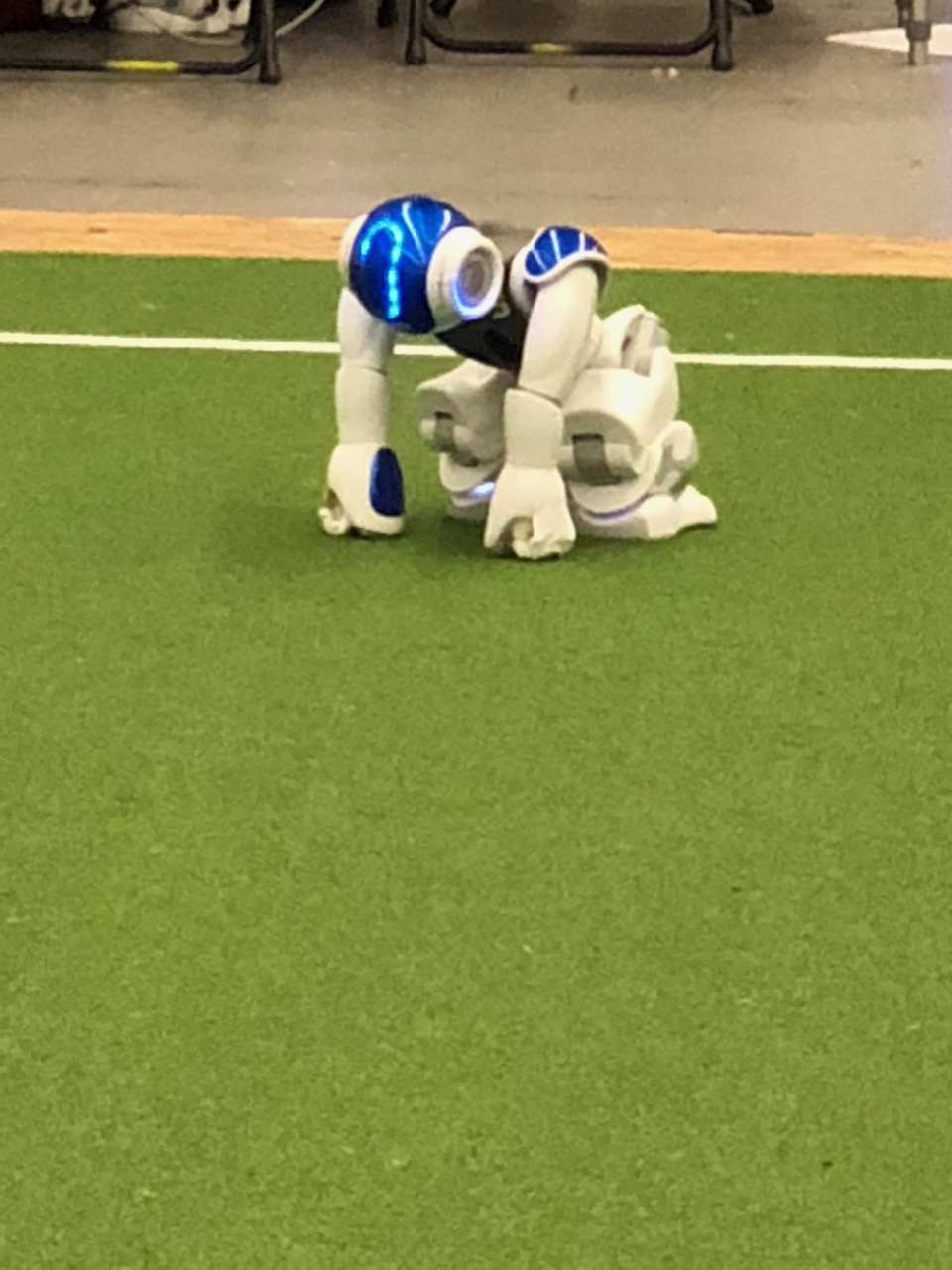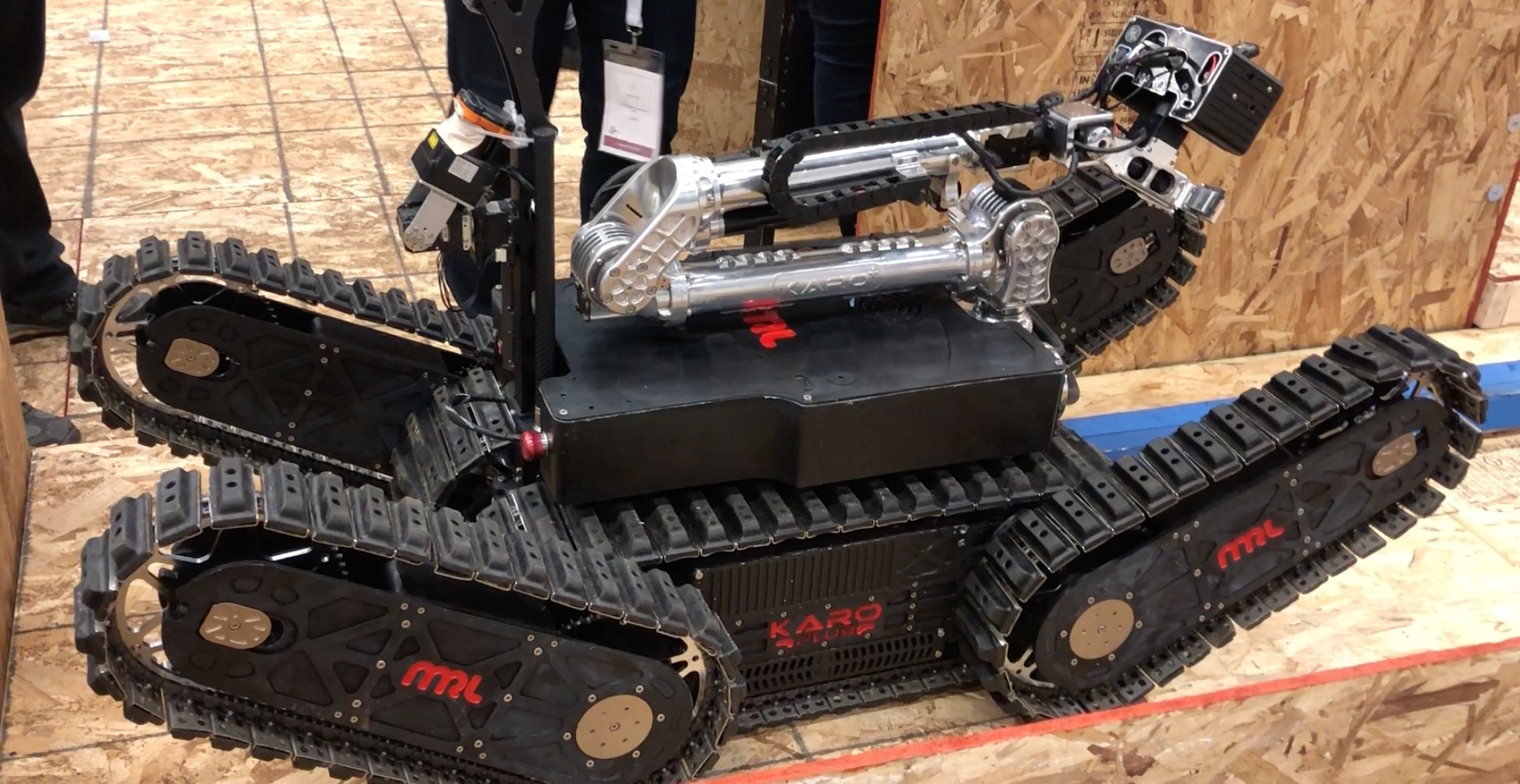
 It has made huge investments into robotics. It will be evident from the following videos that making these investments is critical to succeeding in the near future when we expect a lot of the mundane work to be automated and mechanized.
It has made huge investments into robotics. It will be evident from the following videos that making these investments is critical to succeeding in the near future when we expect a lot of the mundane work to be automated and mechanized.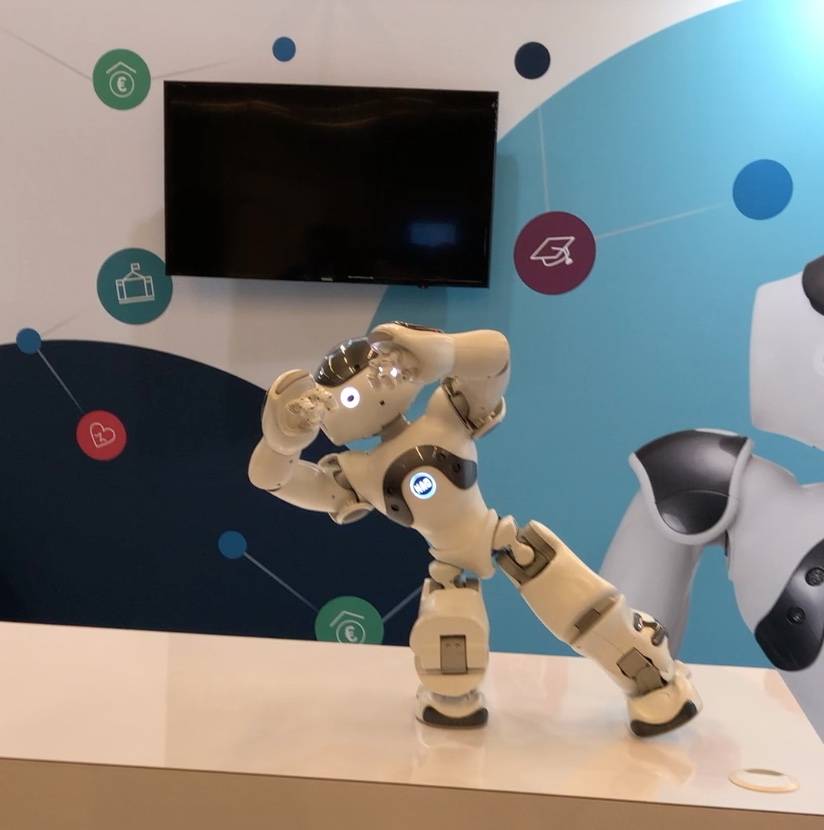
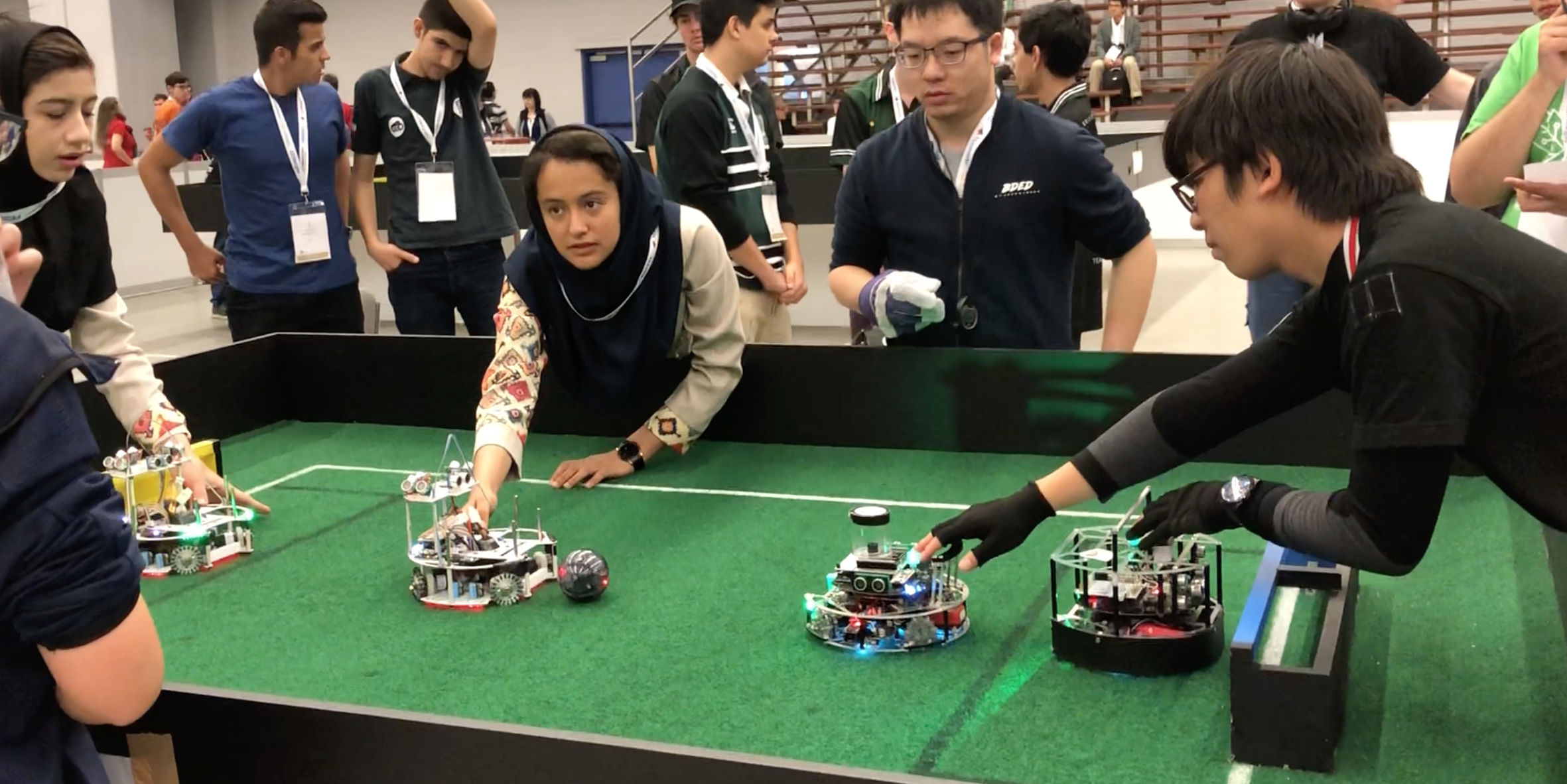
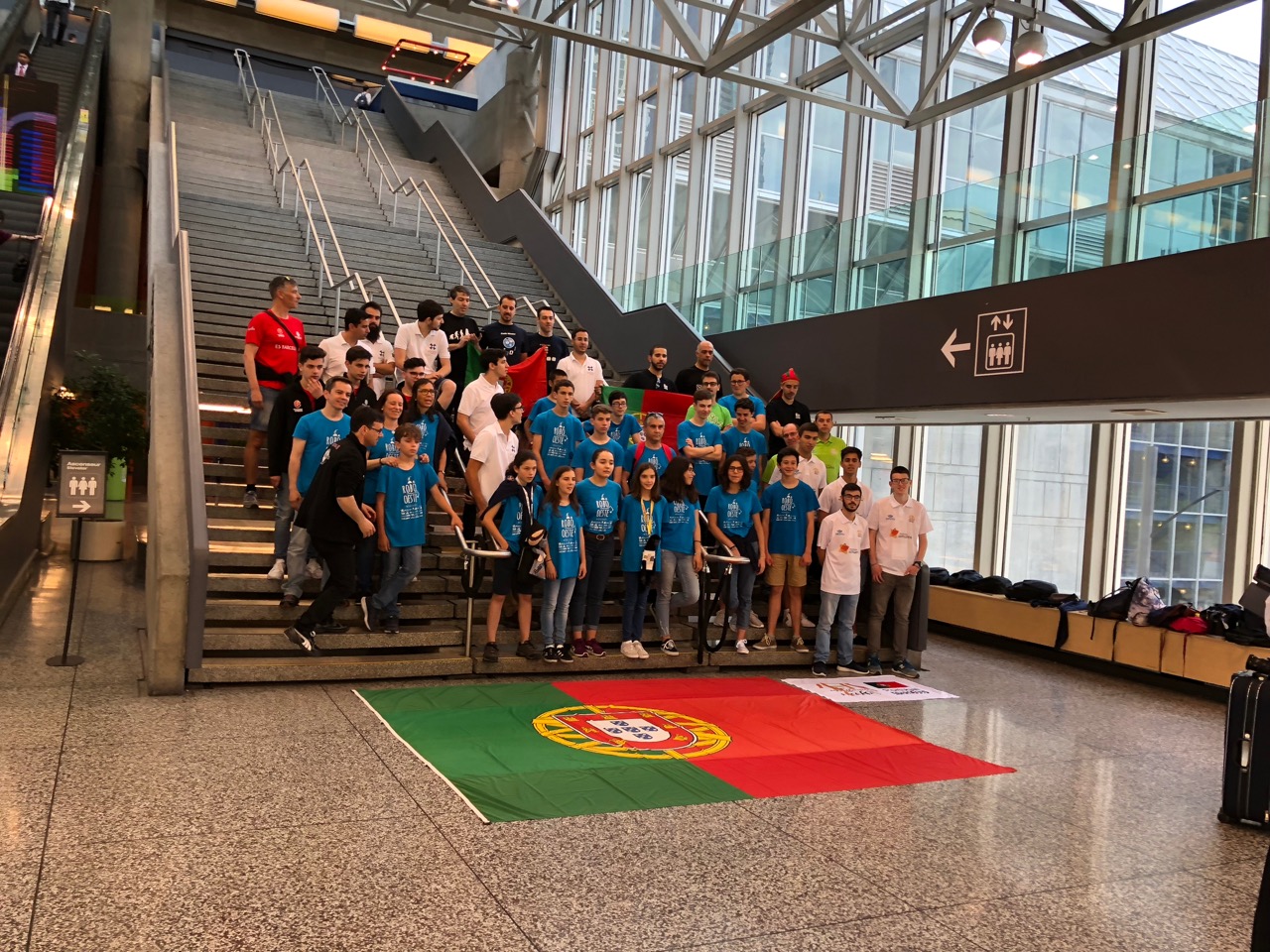 a huge difference in terms of resources and motivation from state sponsorship as was evident with the Iranian, Chinese, Russian, Singaporean, Croatian, Egyptian and Portuguese delegations.
a huge difference in terms of resources and motivation from state sponsorship as was evident with the Iranian, Chinese, Russian, Singaporean, Croatian, Egyptian and Portuguese delegations.

 learn from experience E with respect to some class of tasks T and performance measure P, if its performance at tasks in T, as measured by P, improves with experience E.”
learn from experience E with respect to some class of tasks T and performance measure P, if its performance at tasks in T, as measured by P, improves with experience E.”![\[\theta=(X^TX)^{-1}X^Ty\]](https://eli.thegreenplace.net/images/math/20baabd9d33dcd26003bc44c7d81ba39e1ad4caa.png) ) Refers to a set of simultaneous equations involving experimental unknowns and derived from a large number of observation equations using least squares adjustments.
) Refers to a set of simultaneous equations involving experimental unknowns and derived from a large number of observation equations using least squares adjustments. brains (biological neural networks). Such systems learn the model coefficients by observing real life data and once tuned can be used in output predictions for unseen data or observations outside the training set.
brains (biological neural networks). Such systems learn the model coefficients by observing real life data and once tuned can be used in output predictions for unseen data or observations outside the training set. 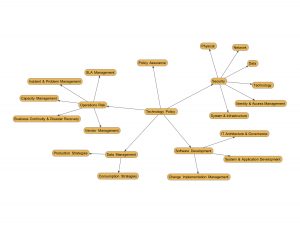
 Common measures that should drive an application or application development team’s metrics collection and measurement:
Common measures that should drive an application or application development team’s metrics collection and measurement: